Structure Problems: Draw Lewis & Line Structures
In these problems you will be asked to draw chemical structures, interconverting between Lewis structures and line structures, drawing the full line structures corresponding to ones that contain abbreviations, and adding lone pairs and assigning charges to atoms.
The fact that the properties of substances are related to their structures at the atomic/molecular level has been called the "central dogma" of chemistry. It follows that being able to interpret and draw representations of chemical structures is a prerequisite to understanding the reactivity of organic compounds.
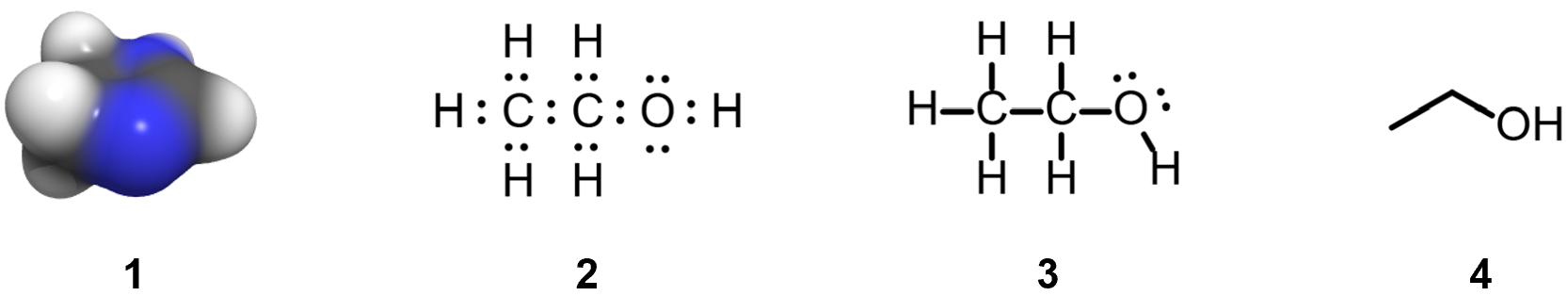
Chemists use a variety of models, of varying sophistication, to represent molecular structure. For example, computer-generated 3D models (1 above) are used to provide 'realistic' images of molecules. Much simpler symbolic representations, such as 'Lewis dot structures' (2), 'Lewis structures' (3) (aka 'Kekule structures') and 'line structures' (4) (aka 'line-bond' or 'skeletal' structures), are easy to draw, and they are routinely used to convey the essential features of molecular structures. Another commonly used style is 'condensed' (CH3CH2OH), and abbreviations are also widely used (EtOH = CH3CH2OH).
Because they are easiest to draw, line structures (4), sometimes with condensed parts and/or abbreviations, and sometimes with the addition of lone pairs (double dots), are the most widely used. However, the omission of C-H bonds in line structures (4) means that it is easy to make mistakes when using them, so understanding what they mean is very important for students of organic chemistry.
The problems on this page will test your understanding of what Lewis structures and line structures represent, your ability to switch between these representations, and your knowledge of the abbreviations used in structures.
On This Page:
You will be given Lewis structures and asked to convert them into line structures, or vice versa.
You will be given line structures that include abbreviations and asked to convert them into full line structures.
You will be given line structures and asked to add lone pairs or charges to the atoms.
Prequisite learning:
- Covalent bonding
- Lewis structures
- The Octet Rule
Learning Objectives:
- Interconvert between Lewis structures and line structures.
- Understand and construct the drawings used to represent the structures of organic compounds.
Free Learning Resources
Organic Chemistry I (Morsch et al.) Drawing Chemical Structures
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry (Reusch) Structural Formulas
Khan Academy Bond-line structures
ChemInfoGraphic Abbreviations
