Mechanisms of Organic Reactions
The mechanism of a reaction is the sequence of steps in the reaction, including details of the bonds are formed and/or broken in each step. Understanding mechanisms is key to understanding the reactions of organic compounds, and is essential to being able to use those reactions to make useful compounds.
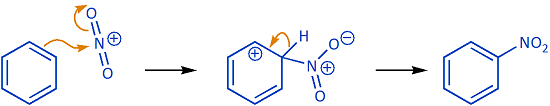
Your task in the problems on this site is to draw chemically reasonable curved (curly) arrows to account for the transformations.
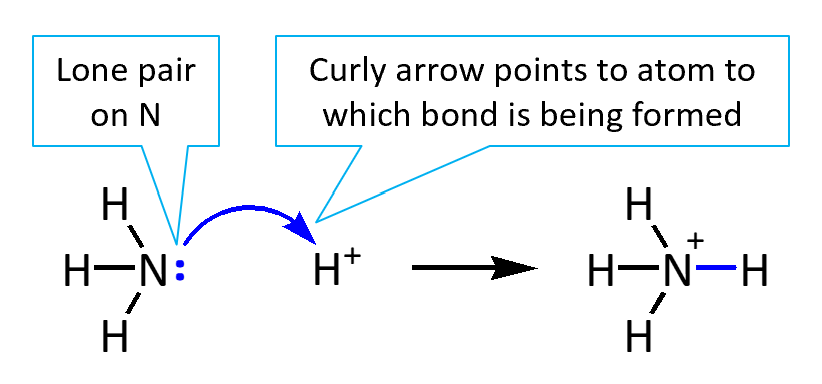
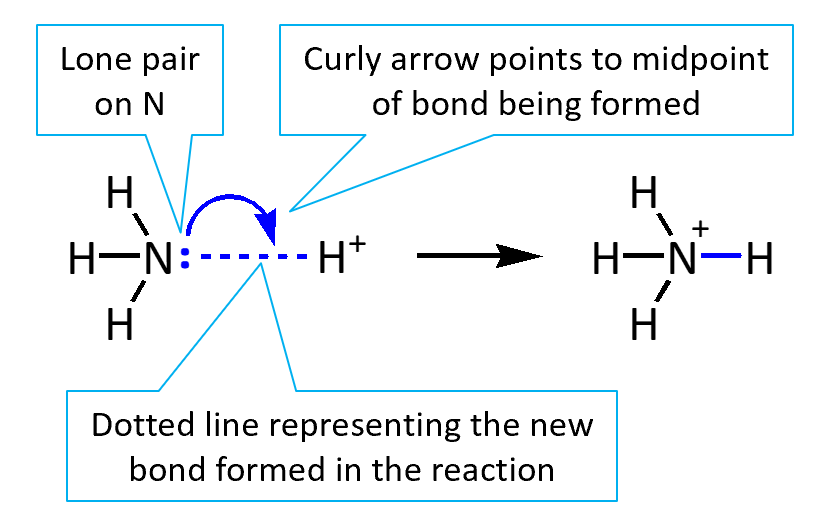
Although the use of curly arrows to show the movement of electrons in organic reaction mechanisms is standard, the details of how they should be drawn are not universally agreed.
Two conventions for drawing curly arrows are available on this site. They differ in how curly arrows representing the formation of bonds between atoms that were not bonded to each other are drawn. Choose one of the two styles below
.